

How to Implement Behavioral Analytics to Detect and Prevent Insider Threats
Insider threats occur when employees, contractors, or trusted individuals misuse their access to harm the organization. The consequences can be severe, financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. According to the Insider Threat Report 2023 by Cybersecurity Insiders, 74% of organizations feel at least moderately vulnerable to insider threats. This vulnerability is often due to user negligence, which caused many malicious insider attacks in 2022.
Human errors and misuse are major factors in data breaches. Verizon’s research highlights that 74% of breaches involve a human element, such as stolen credentials or privilege misuse. These numbers emphasize the need for robust solutions to mitigate insider risks.
Behavioral analytics offers a strategic approach to address this challenge. By monitoring user behavior, it helps detect unusual activities that may signal a potential insider threat. Unlike traditional tools, behavioral analytics identifies patterns, anomalies, and risks before they escalate into breaches.
This article will show you how to implement behavioral analytics effectively, so that you regain control, protect sensitive data, and prevent costly incidents. With the right implementation, you can transform insider threat management into a proactive, results-driven process that safeguards your organization and its future.
Understanding Insider Threats
Insider threats are one of the most complex cybersecurity challenges organizations face today. They involve risks originating from within the organization, often by individuals with legitimate access to systems and data. These threats fall into three main categories:
1. Malicious Insiders
Malicious insiders intentionally exploit their access to harm the organization. They may steal sensitive data, sabotage systems, or leak confidential information. For instance, the JPMorgan Insider Trading Scheme, which involved Ashish Aggarwal, a former analyst at JPMorgan’s San Francisco office, who was charged with insider trading, allegedly used confidential information to trade on non-public information and shared tips with others, including his friend, Shahriyar Bolandian, and his brother, Amit Aggarwal. This scheme generated over $670,000 in illegal profits between 2012 and 2013.


2. Negligent Employees
Not all insider threats are intentional. Negligent employees inadvertently create vulnerabilities through careless actions. These may include mishandling sensitive data, falling victim to phishing attacks, or failing to follow security protocols. According to the 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM Security, phishing and compromised credentials are the most common initial attack methods. These often exploit employee mistakes, making negligence a significant concern.
3. Compromised Accounts
In this scenario, external attackers gain control of an insider’s account. This often happens through stolen credentials or social engineering. Once inside, attackers can operate as legitimate users, making detection difficult. The Scattered Spider attack exemplifies this threat. In September 2023, the cybercriminal group Scattered Spider successfully executed a social engineering attack on MGM Resorts International. The criminals gathered information from an employee’s LinkedIn profile and impersonated them in a call to the help desk, thereby deceiving the support team and gaining unauthorized access to the organization’s network.
Challenges in Detecting Insider Threats
Traditional security methods struggle to detect insider threats. Firewalls and antivirus tools are designed to block external attacks, not monitor internal behavior. Insider threats often involve subtle actions, like unusual file access or minor privilege misuse, which these tools fail to detect.
Additionally, compromised accounts can mimic legitimate user behavior, making detection even harder. Attackers often exploit blind spots in traditional systems, such as a lack of behavioral context. This gap leaves organizations vulnerable to sophisticated insider attacks.
When organizations understand these threats and their challenges, they can better prepare to address them. Behavioral analytics offers a solution by identifying unusual patterns and preventing insider threats before they cause harm.
What is Behavioral Analytics?
Behavioral analytics is a cutting-edge approach to cybersecurity that focuses on understanding user behavior. Unlike traditional security tools, it doesn’t rely solely on predefined rules or static access controls. Instead, it uses data-driven insights to detect and respond to potential threats in real time.
In the context of insider threats, behavioral analytics plays a crucial role. It helps organizations monitor, analyze, and respond to unusual activities that could signal malicious intent, negligence, or compromised accounts.
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) technology uses behavioral analytics to identify patterns and anomalies, enabling proactive protection of sensitive data and systems.
How Behavioral Analytics Works
- Collecting Data from User Activities
Behavioral analytics begins by collecting data from various user activities. This includes login times, file access, application usage, and network interactions. These data points create a comprehensive picture of how users interact with the organization’s systems.
- Identifying Normal Behavior Patterns
Once data is collected, the system establishes a baseline of normal behavior for each user. For example, it learns typical working hours, commonly accessed files, and regular login locations. This baseline serves as a reference point for identifying unusual activity.
- Detecting Anomalies and Potential Threats
When a user deviates from their normal behavior, the system flags it as an anomaly. For instance, accessing sensitive files at odd hours or logging in from unfamiliar locations might trigger alerts. These anomalies are then analyzed to determine if they pose a genuine threat.
Benefits of Behavioral Analytics
Behavioral analytics offers several advantages over traditional security measures. First, it detects threats that static tools often miss, such as insider misuse or subtle privilege escalations. Second, it reduces false positives by focusing on deviations from established patterns rather than generic rules.
Finally, it provides real-time insights, enabling organizations to respond quickly to potential threats. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Organizations can stay one step ahead of evolving cybersecurity challenges by leveraging behavioral analytics.
Steps to Implement Behavioral Analytics for Insider Threat Detection
Implementing behavioral analytics requires a structured approach to ensure effectiveness. Follow these six steps to integrate this powerful tool into your organization’s security strategy.
Step 1: Define Objectives and Identify Threat Scenarios
Start by clarifying your goals and identifying specific insider threat scenarios. Determine what you want to achieve, such as preventing unauthorized data access or detecting privilege abuse.
Outline use cases that align with your organization’s risks. For example, monitoring attempts to access sensitive files outside working hours or tracking unusual privilege escalations. Defining these objectives helps focus your behavioral analytics implementation on areas with the highest impact.
Step 2: Choose the Right Data Sources
Behavioral analytics relies on comprehensive data collection. Identify key data sources to monitor user activities effectively. Examples include:
- Network logs: Track login attempts and access to internal systems.
- Endpoint activity: Monitor device usage and file downloads.
- Application usage: Analyze interactions with specific tools and platforms.
- Email monitoring: Detect phishing attempts and unusual communication patterns.
Selecting diverse data sources ensures a well-rounded view of user behavior.
Step 3: Deploy Tools for Data Collection and Analysis
Choose tools that support behavioral analytics and integrate seamlessly with your existing systems. Modern tools leverage machine learning to analyze large datasets and identify patterns.
Ensure the tools can handle real-time data processing. This capability allows for quicker detection and response to insider threats. A well-integrated solution minimizes gaps and enhances overall security.
Step 4: Establish Baselines for Normal Behavior
Behavioral analytics works by comparing current activities to established baselines. Use historical data to set benchmarks for normal behavior.
For instance, analyze login times, frequently accessed files, and regular application usage. Baselines should account for individual and team-level patterns. By doing so, the system can distinguish between harmless deviations and genuine threats.
Step 5: Implement Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Real-time monitoring is essential for proactive threat detection. Configure the system to flag anomalies as they occur.
For example, Google’s real-time user education program within its email services showcases the power of contextual alerts. It flags suspicious emails and educates users on recognizing phishing attempts. Supported by machine learning, this system adapts to new phishing strategies continuously.
Similarly, your behavioral analytics tools should trigger alerts for suspicious activities, such as accessing restricted files or logging in from unusual locations. Real-time insights allow security teams to act quickly and mitigate risks.
Step 6: Train Teams and Create Response Protocols
Behavioral analytics is only as effective as the people managing it. Train employees and IT teams to recognize insider threats and respond appropriately.
Conduct regular workshops to teach staff about security best practices. Create a clear response plan for handling alerts. For example, define steps for investigating anomalies, revoking access, and notifying relevant stakeholders.
A well-trained team ensures that alerts are acted upon promptly, reducing the risk of insider threats escalating into major incidents.
These step-by-step approaches not only strengthen your cybersecurity posture but also provide peace of mind by proactively addressing insider threats.
Overcoming Challenges in Behavioral Analytics Implementation
Implementing behavioral analytics is a powerful step toward insider threat detection, but it comes with challenges. Addressing these effectively ensures a smooth and impactful deployment.
- Dealing with False Positives and Ensuring Accuracy
False positives can overwhelm security teams and reduce confidence in the system. To minimize these, refine your algorithms to improve accuracy.
Use advanced machine learning models that adapt over time, distinguishing genuine threats from harmless deviations. Regularly review flagged activities and adjust thresholds to match your organization’s risk tolerance. A well-tuned system reduces noise, allowing teams to focus on real risks.
- Addressing Privacy Concerns and Maintaining Employee Trust
Behavioral analytics involves monitoring user activities, which can raise privacy concerns. Employees may feel uneasy about being constantly observed.
To address this, communicate openly about the purpose and benefits of behavioral analytics. Emphasize that the goal is to protect the organization and its employees from threats, not to invade privacy.
Implement anonymization techniques where possible. For example, focus on patterns rather than individual identities unless a threat is detected. Building trust ensures employee cooperation and reduces resistance to the system.
- Scaling Behavioral Analytics for Large Organizations
Scaling behavioral analytics in large organizations can be challenging due to the sheer volume of data.
Adopt cloud-based solutions that handle vast amounts of data efficiently. These platforms offer the processing power needed for large-scale operations.
Use hierarchical baselines that consider department-level and individual patterns. This approach ensures accurate detection across diverse teams and roles without overwhelming the system.
- Ensuring Compliance with Data Protection Regulations
Behavioral analytics must comply with data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Non-compliance can lead to fines and reputational damage.
Ensure your tools are designed to meet regulatory requirements. For example, encrypt sensitive data and limit access to authorized personnel using technologies like Identity Access Management (IAM).
Regularly audit your systems to ensure compliance and stay updated on changing regulations to avoid potential pitfalls.
Addressing these challenges ensures that behavioral analytics is implemented effectively and responsibly.
Top 5 Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions
EDR tools, powered by behavioral analytics, offer advanced threat detection and rapid response capabilities, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring business continuity. Let’s take a look at the top 5 tools:
1. Xcitium EDR (Overall Best EDR Solution)


Xcitium EDR is recognized for its innovative approach to cybersecurity. It combines cutting-edge technology with a user-centric design, ensuring robust protection against even the most sophisticated threats. A standout feature of Xcitium is its Auto Containment solution, which isolates potential threats in real time. This proactive mechanism ensures that malware or other malicious activities are contained before they can disrupt operations.
Key Features of Xcitium EDR
I. Real-Time Threat Detection
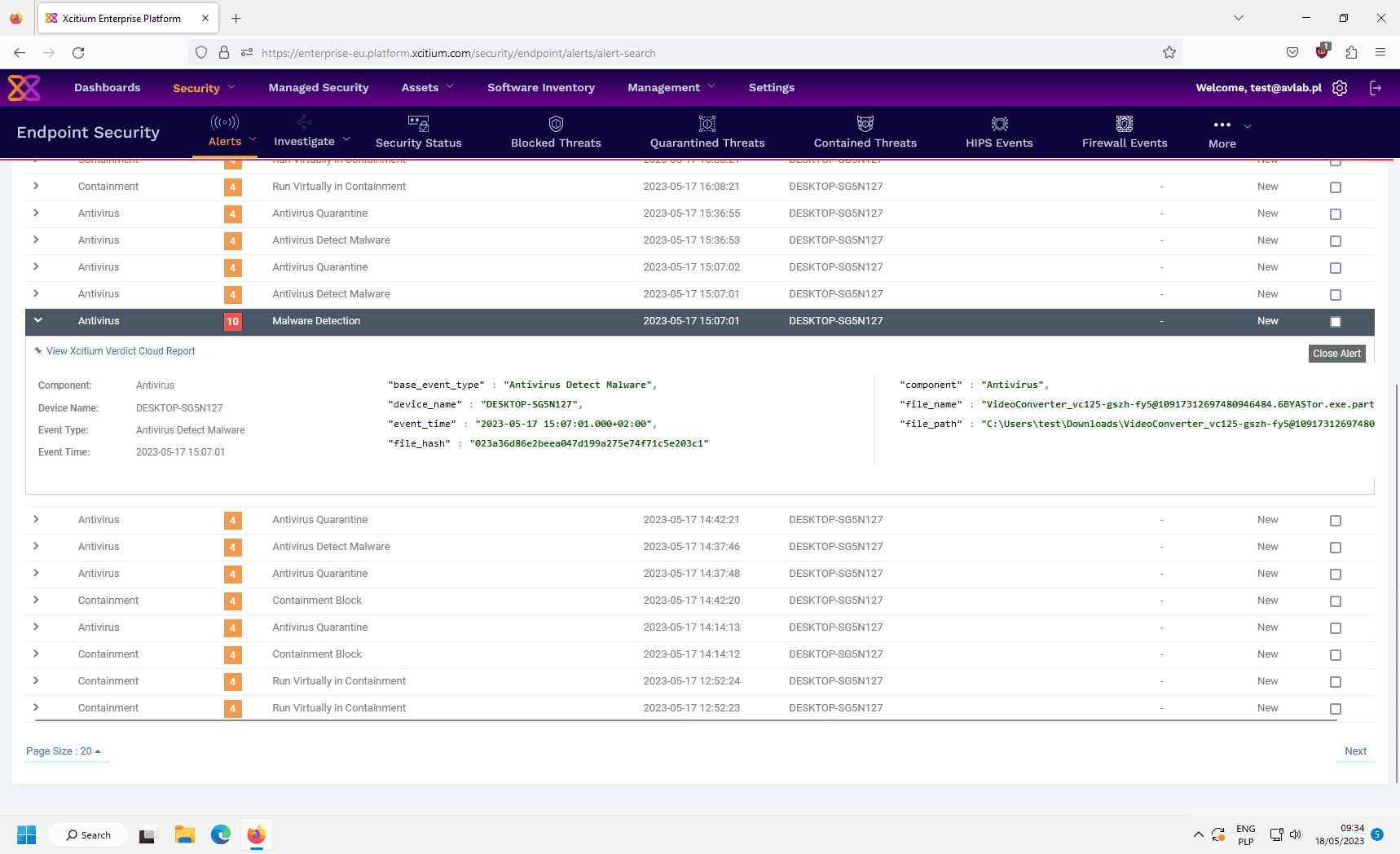

The interface highlights critical features that enhance the detection process:
Alert Categorization
The software categorizes alerts by type, such as “Antivirus Quarantine” and “Containment.” This organization provides security teams with a clear snapshot of ongoing security events, enabling them to assess the nature and scope of potential threats quickly.
Event Details
Each alert entry includes detailed information, such as the event type, timestamp, and affected device (e.g., “DESKTOP-SG5N127”). Additionally, technical data like the file hash of detected malware is displayed, giving security analysts the context needed to evaluate the severity of the incident.
Filtering and Sorting
Xcitium’s filtering and sorting capabilities allow users to sift through alerts based on event type, timestamp, or device. This feature prioritizes critical alerts, enabling faster response times and reducing the likelihood of missed threats.
Investigation Tools
The “Investigate” tab offers tools for in-depth analysis of specific alerts. Security analysts can explore event details, assess the threat level, and determine appropriate response actions.
II. Advanced Malware Protection
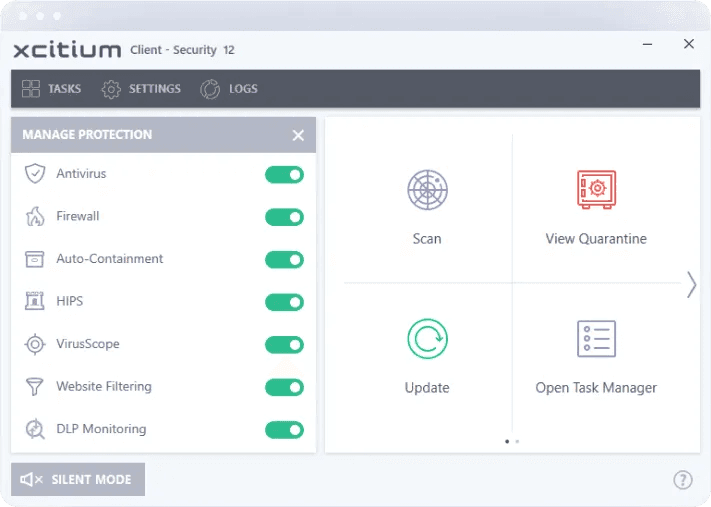

The interface showcases several key features that enhance the effectiveness of malware protection:
Security Module Toggles
Prominent on/off switches for security modules such as Antivirus, Firewall, and Auto-Containment provide an intuitive way to manage protection layers. This flexibility allows administrators to customize the security configuration to meet specific organizational needs.
Quick Action Buttons
The “Scan,” “View Quarantine,” and “Update” buttons offer quick access to essential security functions. Administrators can initiate system scans, review quarantined files, or update security definitions with a single click.
Silent Mode
The Silent Mode toggle is a practical feature that temporarily disables certain notifications or alerts. This is particularly useful during presentations or critical workflows, ensuring end-users are not distracted by security alerts while maintaining full protection in the background.
III. Comprehensive Device Management
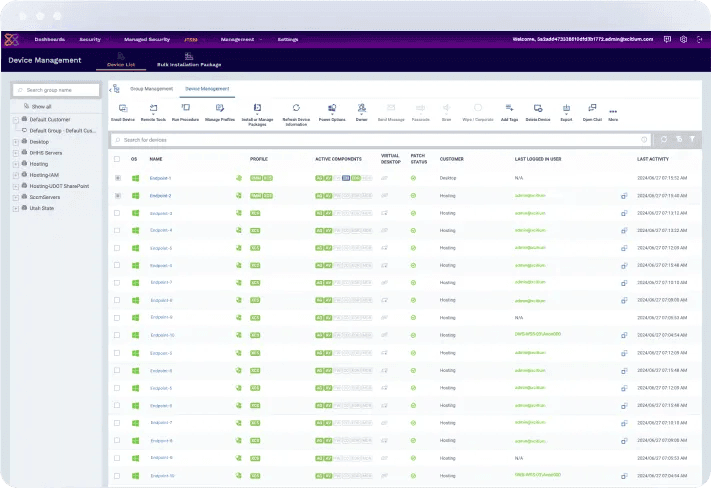

The interface highlights several features that make device management efficient and intuitive:
Device Group Management
Administrators can create, edit, and manage groups of devices directly from the dashboard. This functionality allows for the application of specific policies and configurations to targeted device groups, ensuring that each department or team has tailored security settings.
Software Distribution
The “Installation Package” section enables administrators to create and deploy software packages to devices within specific groups. This feature ensures seamless updates and installations across the organization, eliminating the need for manual intervention on individual devices.
Device Status Monitoring
Columns displaying critical data such as “Active Components,” “Last Login,” and “Last Activity” provide real-time insights into device performance and security status. These details allow administrators to quickly identify devices that require updates, show unusual activity, or have inactive security components.
IV. Automated Incident Response
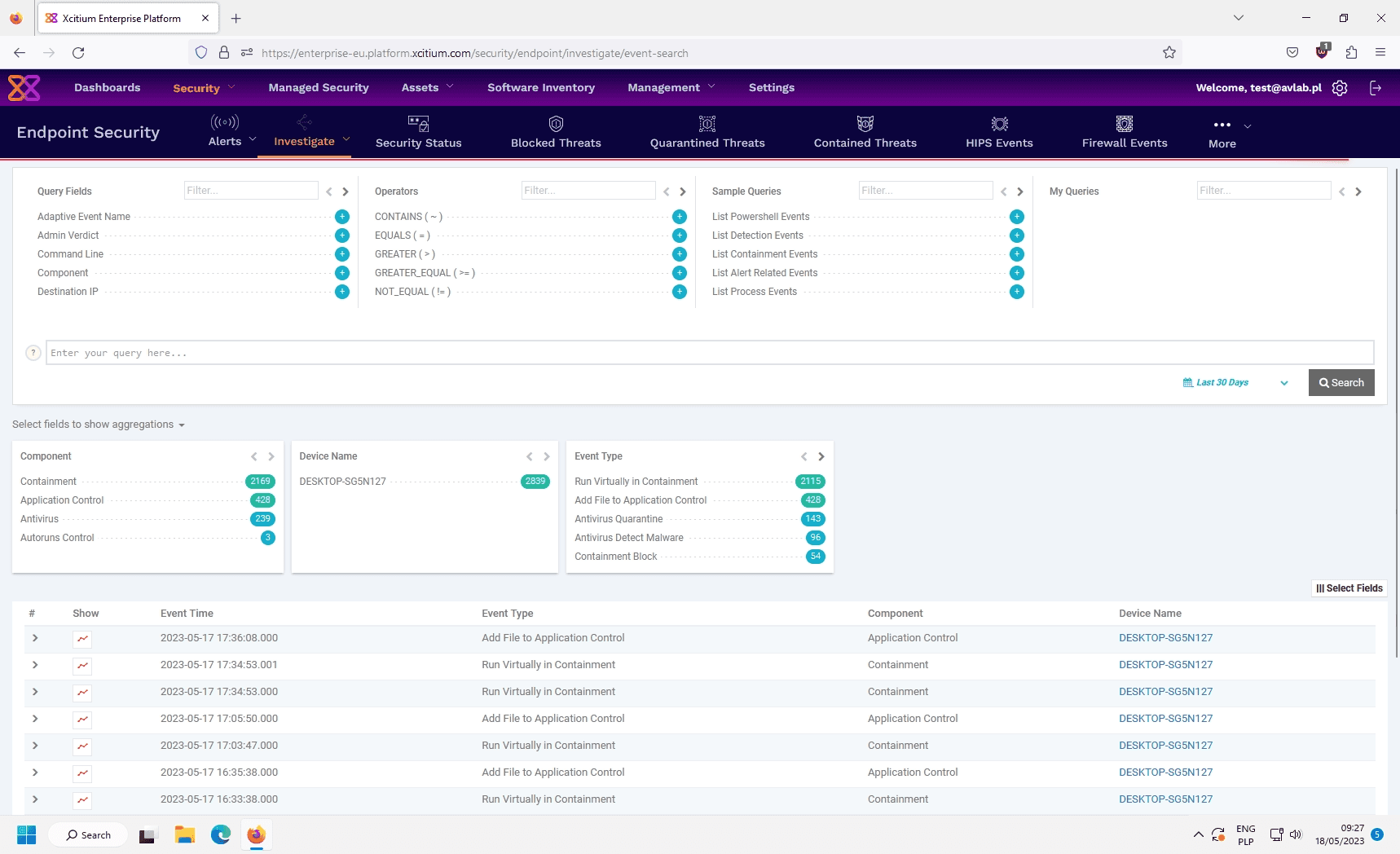

The interface showcases advanced features to streamline the incident response process:
Query Builder
The Query Builder provides a user-friendly interface for creating precise and complex queries to filter and analyze security events. With a wide range of operators such as “EQUALS,” “GREATER THAN,” and “NOT EQUAL,” and fields like “Device Name,” “Event Type,” and “Component,” administrators can refine search criteria to pinpoint critical incidents.
Event Data Visualization
The query results are displayed in a detailed table, presenting essential information such as event type, timestamp, component, and device. This comprehensive visualization provides a clear overview of security events, helping teams quickly assess the scope and nature of an incident.
Aggregation and Trend Analysis
Xcitium allows analysts to aggregate and visualize data trends by selecting fields such as “Device Name” or “Event Type.” This functionality highlights patterns in security events, enabling teams to detect anomalies or recurring issues. For instance, if multiple devices show similar suspicious activity, it could indicate a coordinated attack that requires immediate intervention.
V. Cloud Security
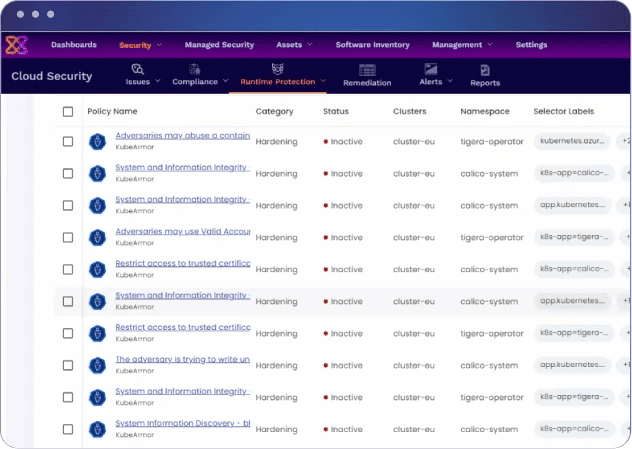

The interface showcases key cloud security features, enabling robust protection:
Policy Management for Proactive Defense
The Xcitium dashboard features a robust Policy Management system that categorizes security policies by purpose, such as “Hardening” or “System and Information Integrity.” Each policy is marked with its status, such as “Active” or “Inactive,” providing administrators with a clear view of the organization’s current security posture. This enables teams to implement and enforce policies that align with their specific cloud security needs.
Issue Tracking for Immediate Insights
The Issues tab provides a detailed overview of detected security issues, including their severity, location (e.g., clusters, namespaces), and potential impact. This feature empowers security teams to prioritize vulnerabilities based on their risk level, ensuring that critical threats are addressed promptly.
Pricing
Xcitium’s pricing is designed to cater to diverse organizational needs, starting at $259/year for the Xcitium Managed plan. This includes 24/7 expert-led threat detection and response, Zero Trust Containment, and proactive threat hunting, perfect for businesses without an in-house SOC.
For broader protection, the Xcitium Complete plan is available for $279/year and offers cross-layered detection across endpoints, networks, and cloud environments.
Additional packages tailored to specific functions or scales are also available. Click here to learn more.
2. FortiEDR (Best for Fortinet Ecosystem Users)

FortiEDR is part of Fortinet’s Security Fabric, making it a natural choice for organizations already using FortiGate firewalls. This solution offers threat intelligence, USB device control, and customizable detection rules, ensuring robust endpoint protection. It also supports threat hunting, empowering security teams to identify vulnerabilities proactively. FortiEDR seamlessly integrates with other Fortinet products, providing a unified security approach.
Pricing: Custom pricing available; contact Fortinet for a quote.
3. Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR (Best for Advanced Security Teams)

Cortex XDR by Palo Alto Networks is ideal for enterprises with tech-savvy IT teams. It excels in sandboxing, forensics tools, and comprehensive threat detection. Recognized for its perfect MITRE test scores in 2023, this platform ensures unmatched protection. Large organizations seeking scalable, enterprise-grade security will find Cortex XDR a valuable investment.
Pricing: Custom pricing available; contact Palo Alto Networks for a quote.
4. CrowdStrike Falcon Insight XDR (Best for Threat Hunting)

CrowdStrike Falcon Insight XDR provides a cutting-edge approach to threat detection and response. It includes automated threat response, real-time threat intelligence, and advanced hunting tools. This solution is perfect for organizations requiring proactive security measures against evolving threats. Its lightweight architecture ensures minimal impact on system performance.
Pricing: Custom pricing available; contact CrowdStrike for a quote.
5. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint & XDR (Best for Administrative Features)

Microsoft Defender combines endpoint, cloud, and identity protection with administrative tools like dashboards and policy creation. Its consistently high MITRE scores and integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem make it an excellent choice for businesses of all sizes. The solution offers 30-day free trials, making it accessible for evaluation before commitment.
Pricing: Free trial available; contact Microsoft for a custom quote.
Final Thoughts
When selecting an EDR solution, prioritize features like real-time threat detection, automated incident response, comprehensive device management, and advanced malware protection. These capabilities are essential for proactively identifying and neutralizing threats before they escalate into breaches.
Also, Xcitium EDR simplifies insider threat detection with AI-driven capabilities that supplement traditional malware detection methods. This ensures protection against zero-day attacks and evolving malware variants, keeping your organization secure from all angles.
Ready to see how Xcitium can transform your security strategy? Request a free demo today and experience unparalleled endpoint protection firsthand.
About The Author
Ibrahim crafts high-performance content that connects brands with their audiences and drives impactful results. He has extensive writing experience across various niches, including SaaS, Technology, ESG, Sustainability, Biodiversity, and Lifestyle. His track record of earning five-star ratings from clients serves as proof of his unwavering commitment to excellence.
If you’d like to be a freelance journalist, writer, or weekend warrior with Cyber News Live, please email us at contact@cybernewslive.com. Thank you!
